
You might not often find yourself thinking about the zinc kettle at all. Did you know that it is an important element in the zinc galvanizing process, through which steel and iron are protected from rust and corrosion?
The latter can be explained by the fact that for those of us who are not employed in heavy industry, galvanization remains a somewhat exotic process. However, it is a very important process that enables long life spans of products ranging from guard rails to street lamps to air conditioning units, among others.
In the next part of the article, let us look at what galvanization is all about and how the zinc kettle plays an important role. We will discover how molten zinc from the kettle reacts with steel to form a zinc layer on the steel surface.
And we will find out why zinc protects iron and steel so efficiently, even in the most aggressive conditions. It is amazing that a simple metal bucket can also serve an important role and aid in contributing to structures that last for generations.
An Overview of Galvanization and Why Zinc Is Used
Galvanization is the process of creating a thin layer of zinc on a surface of iron or steel to prevent rust formation. The general hot-dip zinc galvanizing is done whereby the metal is immersed in a basin with molten zinc. It forms a protective layer on the surface of the metal and develops a layer of zinc, which is very strong and does not get corroded easily.
The Role of Zinc Kettles in the Galvanization Process
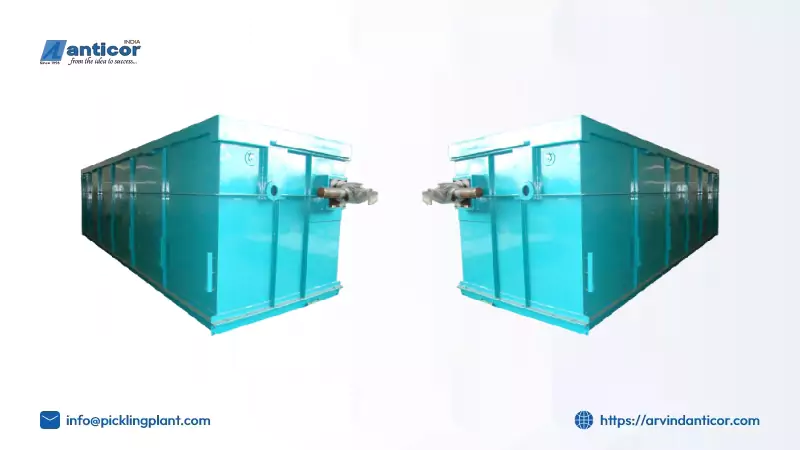
The zinc kettle is the equipment where the molten zinc bath is made, with the help of which the steel parts can be submerged. The kettle must be able to resist extremely high temperatures and melting or rusting; this is why most of them are made from cast iron or steel with an inner lining of refractory brick.
The kettle has features to regulate the zinc bath temperature, about 860°F, and carry drums or forks for handling the steel parts. The kettle offers protection for the galvanizing reaction since it is able to restrict access to oxygen.
Zinc is melted, and when immersed in the molten zinc, the zinc forms a metallurgical bond to the steel surface to form several layers of iron-zinc alloy. It’s important to consider the type of kettle used depending on the size and shape of the parts to be galvanized.
Larger kettles may have a design associated with structural steel shapes, whereas smaller kettles are intended for fasteners and sheets. The kettle must be maintained well, and the chemical composition of the molten zinc bath has to be regulated to the right standards to yield a high-quality and equally thick layer of galvanized coatings.
The presence of impurities in the zinc bath results in a dull surface, porous coating, or flaky coating on the substrate. The temperature of the zinc bath has also to be in the required range, depending on the thickness and type of galvanizing to be provided.
What Made It Possible to Galvanize with Zinc Kettles?
The hot-dip zinc galvanizing process involves the use of dipping steel in molten zinc for the purpose of obtaining a protective layer against corrosion. Zinc kettles in the galvanization process are a crucial component of the heating and maintenance of the zinc required for the process.
Large Throughput for Liquid Zinc
Zinc kettles are massive vessels, usually 10 feet in diameter and 10 to 15 feet in depth, capable of containing up to a hundred tons of molten zinc at about 460 °C. Such an impressive capacity enables one to increase members such as beams, pipes, and sheet piles. These kettles are made of steel and refractory substances that do not degrade even at high temperatures.
Efficient Heating And Temperature Control
Multiple burners heat the zinc kettles, often using propane or natural gas. Computerized systems precisely control the burners to maintain the optimal temperature for galvanizing. Insulated kettle walls, lids, and space underneath the kettle help retain heat, reducing energy usage. Built-in thermocouples provide constant temperature feedback to automatically adjust the burners.
Safe Handling of Molten Metal
Safety mechanisms like fume extraction systems remove toxic zinc fumes, while rigging equipment enables safely submerging and retrieving steel parts. Kettles may have mechanisms to filter out zinc dross, the impurities and oxides that form on the zinc’s surface.
With the right equipment and safety precautions in place, zinc kettles facilitate dipping steel in molten zinc on an industrial scale. Their extreme heat capacity, advanced control systems, and safety mechanisms enable efficient, high-volume galvanization to protect steel from corrosion. The role of zinc kettles is pivotal to this widely used rust-proofing process.
The Step-by-Step Zinc Kettle Galvanizing Method
To galvanize steel using the zinc kettle method, several essential steps must be followed carefully. First, the steel parts are cleaned and prepared. Then, the galvanization method can begin.
Cleaning and preparing the steel
The steel parts are scrubbed clean of dirt, grease, and oils. Any surface rust or mill scale is removed through sandblasting or acid pickling. The goal is to have a perfectly clean, bare steel surface for the zinc to adhere to.
Heating the zinc
Copper is then poured into flat, rectangular shapes called anodes, which are made from zinc ingots, and smelted by heating in kettles to around 860 °F or until the zinc melts and forms a molten liquid.
During the process, when zinc is melted, all the strains, dross, and other impurities rise to the surface of the liquid metal and are removed. Several fluxing agents are incorporated to strip the zinc of its oxygen, which might produce a poor coating.
Coating the steel
The clean steel parts are submerged in the molten zinc bath using cranes or conveyors. They remain submerged until they reach the same temperature as the zinc. When withdrawn, a smooth, uniform coating of zinc adheres to the steel. The zinc hardens instantly as the part cools.
Inspecting the Finish
The newly galvanized parts are inspected to ensure complete, high-quality coverage. Parts that lack zinc adhesion or have rough, porous surfaces may need to be re-dipped. Properly coated parts will have a bright, shiny finish and a smooth surface.
Sealing and packaging
Once cooled and inspected, the galvanized parts may receive a sealant to prevent the formation of zinc hydroxide. They are then packaged to prevent damage to the new coating during storage and transport.
By closely following each step in the zinc kettle galvanization process, high-quality hot-dip galvanized steel parts can be produced efficiently and economically. The end result is steel that boasts an attractive, durable zinc coating with superior corrosion resistance.
The Benefits of Using Zinc Kettles for Galvanization
Galvanization requires molten zinc and a catalytic reaction to adhere the zinc coating to steel. Zinc kettles provide an ideal container for this process.
Superior heat conduction
Zinc kettles efficiently conduct and distribute heat, allowing the zinc to remain in a molten state at around 870°F. Their metallic construction also means they can handle the high temperatures needed for galvanization without warping or melting.
Long-lasting and durable
Due to their high melting point, zinc kettles are able to cope with the high temperatures that are necessary during the galvanization process repeatedly, batch after batch. They also do not corrode or oxidize, even under conditions that involve running molten zinc on them on a continuous basis. Given adequate care and attention, the longevity of a zinc kettle is said to be between three and five years in a galvanizing plant.
Safe and environmentally friendly
Unlike kettles made of certain other materials, zinc used for galvanizing kettles does not release toxic fumes or chemicals when exposed to high heat. Zinc and its alloys are also fully recyclable, so kettles that eventually need replacement can be reprocessed and made into new products. This sustainability helps galvanizers meet environmental standards and regulations.
Cost-effective in the long run
While zinc kettles have a higher upfront cost than some alternatives, their durability and longevity mean significantly lower costs over time. They also help improve the galvanization method’s efficiency, reducing wasted resources and additional costs. For high-volume galvanizers, the savings can be substantial.
By providing an ideal vessel for holding and heating zinc, zinc kettles enable an efficient, cost-effective galvanization process with environmental benefits. For these reasons, most industrial galvanizers rely on zinc kettles as a key part of their operations. With the right care and maintenance, zinc kettles should continue enabling high-quality galvanization for years to come.
Conclusion
So, there you have it. The zinc kettle plays a crucial role in the electrolysis process of the galvanization process. Some of its features include: it effectively regulates the temperature of the fluid and the distribution of zinc, enhancing the coating of the surface.
And the smooth zinc used for galvanizing coatings keeps the steel protected from rust and corrosion. At Arvind Anticore, we understand that hot dip galvanizing plants require efficient zinc kettles, and we provide the most effective and efficient zinc kettles for the production of the best products. Through incorporating our zinc kettles, manufacturers will realize a vast improvement in terms of the efficiency of their galvanization process, thereby increasing output and reducing costs.
For more details about how our zinc kettles may be beneficial to your galvanization process, please feel free to contact Arvind Anticore at your earliest convenience. We are leading hot dip galvanizing plant manufacturers and have professionals who are ready to attend to your every need and offer you the best solutions.
Let’s Connect
Contact Us
We are live 24/7 and reply within 48 hours.
Get in Touch
-
-
-
Address
Survey No.584/1+2 – C,Nr. Akshar Industrial Estate Mahemdabad Highway Road,Vatva Ahmedabad-382445, Gujarat, India.